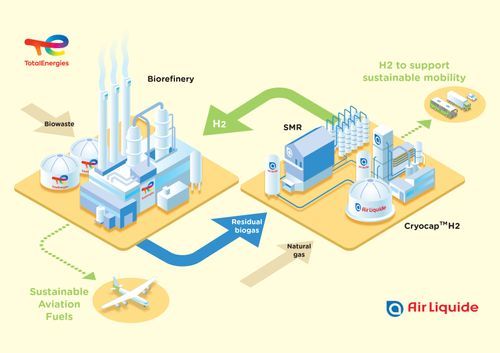
TotalEnergies and Air Liquide will produce renewable, low-carbon hydrogen at the Grandpuits zero crude platform, a refinery near Paris, according to a press release.
Under a long-term contract committing TotalEnergies to purchase the hydrogen produced for the needs of its platform, Air Liquide will invest over €130m in the construction and operation of a new unit producing hydrogen. This unit will partly use biogas from the biorefinery built by TotalEnergies and will be delivered with Air Liquide’s carbon capture technology Cryocap.
These innovations will prevent emissions amounting to 150,000 tons of CO a year compared to current processes. TotalEnergies’ biorefinery will use the unit’s hydrogen to produce sustainable aviation fuel.
In line with the two companies’ shared ambition to get to net zero by 2050, the project includes sustainable and circular innovations:
- The new hydrogen production unit, with the capacity to produce over 20,000 tons a year will produce hydrogen that is partly renewable, thanks to the recycling of residual biogas from the Grandpuits biorefinery, in place of the natural gas that is normally used.
- This unit will be delivered with a carbon capture technology, allowing it to help reduce the platform’s carbon footprint, by capturing over 110,000 tons of CO2 a year for reuse in food and industrial applications.
- Most of the unit’s renewable, low carbon hydrogen will be used by the biorefinery itself, to produce sustainable aviation fuel, but it could also be used to support sustainable mobility in the Ile-de-France region.
“By recycling the biogas produced by the biorefinery into renewable hydrogen, this innovative project makes full use of the conversion of the Grandpuits refinery into a zero crude platform harnessing the potential of biomass, especially in the production of sustainable aviation fuel,” said Bernard Pinatel, president, refining & chemicals, TotalEnergies. “Combined with the production of low carbon hydrogen and the capture of CO2, this project contributes to TotalEnergies’ ambition to decarbonize all of the hydrogen used by its European refineries by 2030.”
“This innovative project is characterized by the combination of several solutions in order to produce renewable and low-carbon hydrogen,and contribute to the decarbonization of TotalEnergies’ Grandpuits site. It also provides the opportunity to recycle CO2 as part of a circular economy approach while securing its supply for agri-food applications. This project illustrates Air Liquide’s expertise in working with its customers on customized solutions to help them reduce their carbon footprint and actively participate in the fight against global warming. It provides yet another example of the key role that hydrogen will play to succeed in the energy transition”,” added Pascal Vinet, senior vice president and member of the executive committee, Air Liquide, in charge of Europe industries activities.